Git
Git 原理 #
git 是一个内容可寻址文件系统,核心是一个简单的 key-value 存储
有向无环图
.git 目录解读 #
HEAD #
指向当前分支的指针
objects/ #
当前 repo 的所有对象存储
SHA-1 checksum of the content and its header
refs/ #
所有指针
index #
暂存区,变动的暂存区
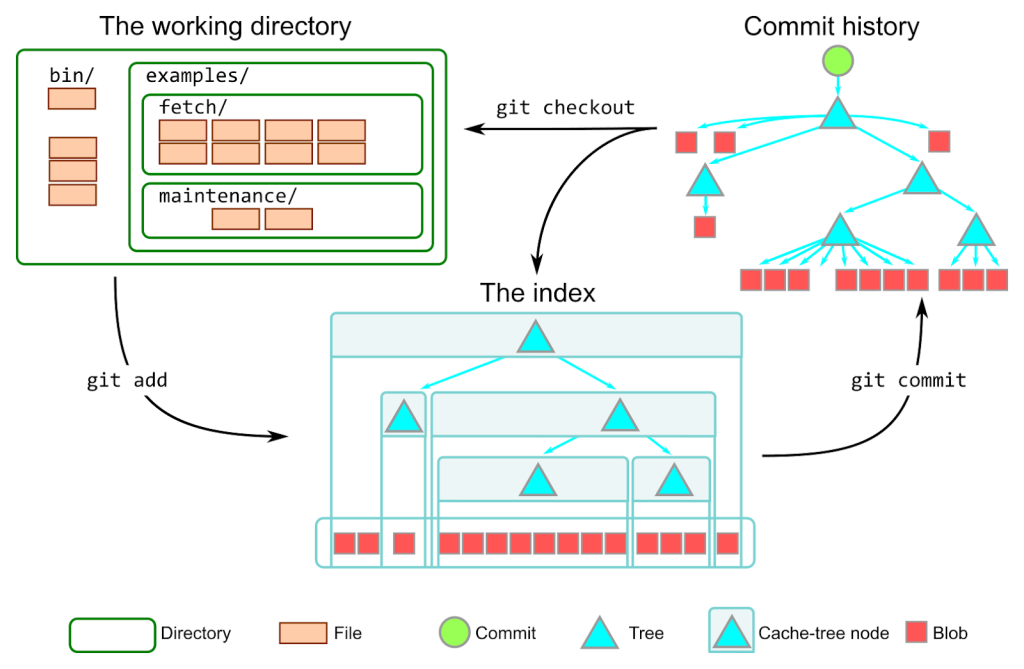
working directory -> index -> repository
git add 后,文件会被 hash 然后存到 index 区
git commit 时,index 区的内容被用来创建新的 commit
git checkout 时,commit 的数据被写入到 working directory 和 index
概念 #
Working directory #
当前分支 object tree 的检出副本,可编辑,可被 commit
Object 类型 #
Tree object #
目录存储为 tree
A tree is a simple list of trees and blobs that the tree contains, along with the names and modes of those trees and blobs
Blob object #
存储文件内容,文件 name 和 mode 不与 blob 一起存储
Commit object #
包含下面这些内容
- tree
- author
- committer
- message
- parent commit sha1 (如果有)
Tag object #
针对某个 commit 的持久别名
Branch #
Creating a branch is nothing more than just writing 40 characters to a file.
Remotes #
git 命令 #
fetch #
从远端拉取本地没有的 refs 和 objects,远端默认叫 origin,也可以任意命名,可以有多个远端
merge #
fast forward:
the commit on the branch you’re on is a direct ancestor of the branch you’re merging in
when you try to merge one commit with a commit that can be reached by following the first commit’s history
rebase #
比 merge 的 history 更清晰
git rebase <baseBranch>
Do not rebase commits that exist outside your repository and that people may have based work on.